Which Bolt and Fastener Strengths Ensure Project Safety?
What Are Bolt and Metal Fastener Strengths?
When it comes to Industrial Bolt & Fastener Strengths, understanding the strength of industrial metal fasteners is essential for engineers, construction teams, and manufacturers. Whether you’re working with A325 bolts, high-strength structural bolts, or custom rivets, knowing the differences between tensile strength, shear strength, and proof load helps ensure assemblies remain safe and reliable. Metal fasteners—from grooved pins to stainless threaded inserts—are all designed with specific strength limits, and overlooking these limits can compromise safety and long-term durability. Welleshaft specializes in supplying metal fasteners built to exact specifications, ensuring consistent performance, compliance, and confidence in critical applications.
What is Bolt Strength?
Bolt strength defines the maximum load a bolt or fastener can withstand, including tension, shear, and bending. Engineers and construction teams use this knowledge to ensure steel structural bolts, heavy hex bolts, and precision fasteners like stainless screw inserts and slit bolts keep bridges, buildings, and machinery safe. By following standards like Eurocode 3 (EN1993) or AISC 360-10, they ensure bolted connections meet requirements, resist operational loads, and prevent loosening or deformation. Choosing high-quality industrial metal fasteners from trusted suppliers like Welleshaft secures structural integrity and long-term reliability.
What Is Tensile Strength for Metal Fasteners?
A fastener’s tensile strength, also called ultimate tensile strength (UTS), is the maximum force it can withstand before breaking. Factors like material, hardness, and size affect this. Understanding Industrial Bolt & Fastener Strengths helps engineers select the right A325 or A490 bolts, clevis pins, or custom metal fasteners for heavy-duty applications, ensuring safe, reliable performance and preventing overloading or deformation.
Tensile strength isn’t just a number—it’s defined by quality standards like ISO, ASTM, and SAE to classify fasteners by grade. For example, ISO 898-1 specifies minimum tensile strengths for bolts based on diameter and property class:
| ISO 898-1 Property Class | Min. Tensile Strength (≤16mm) | Min. Tensile Strength (>16mm) |
| Class 8.8 | 800 MPa | 830 MPa |
| Class 10.9 | 1,040 MPa | 1,040 MPa |
| Class 12.9 | 1,220 MPa | 1,220 MPa |
By following these standards, designers can calculate loads accurately, select high-strength metal fasteners, and maintain safety in structural and mechanical projects. Choosing fasteners that meet specified tensile requirements ensures durability, reliability, and compliance across metal fastenings, grooved pins, slit bolts, and stainless steel threaded inserts.
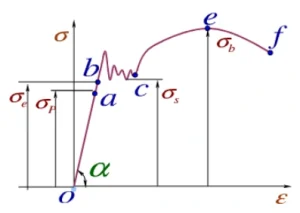
How Do We Measure Bolt Strength Parameters?
Measuring Industrial Bolt & Fastener Strengths involves calculating tensile area, testing shear, and determining proof load. Engineers use standard formulas or bolt load calculators for fasteners like grooved pins, split bolts, or threaded inserts, ensuring they meet project requirements and support safe structural design.
How to Calculate Tensile Strength?
Tensile strength measures the maximum pulling force a bolt or fastener can withstand and plays a key role in Industrial Bolt & Fastener Strengths. Engineers calculate it using P = St × As, considering material, diameter, and thread design, to ensure fasteners like A325 bolts, grooved pins, or stainless threaded inserts perform safely in heavy-duty structures and machinery, following standards like AISC 360-10.
How is Shear Strength Determined?
Shear strength is the maximum load a bolt or fastener can handle perpendicular to its axis and is vital for assessing Industrial Bolt & Fastener Strengths. Typically lower than tensile strength, misjudging shear can cause joint failures in structures, machinery, or electrical systems. Engineers calculate it using Fs = A × τ × n, considering bolt type, arrangement, and load path for safe, reliable connections with fasteners like grooved pins, split bolts, or stainless threaded inserts.
What is Proof Load of a Bolt?
Proof load is the maximum stress a bolt or fastener can handle without permanent deformation. Calculated as Fp = At × Sp, it is typically 85–95% of a bolt’s yield strength and helps engineers set safe torque, preventing elongation, loosening, or failure in structural and machinery applications.
How Are Fasteners Tested and Verified?
Testing fasteners is essential for quality assurance. Common methods include the wedge tensile test, Junker test, and inspection of thread strength. For specialized fasteners like stainless steel threaded inserts for metal or custom standoffs, Welleshaft ensures each batch passes strict testing before shipping. This guarantees that your industrial metal fasteners meet performance requirements.
How Do You Determine the Tensile Strength of Fasteners?
Tensile testing measures how much pulling force a metal fastener can handle before failure. Using methods like the wedge tensile test, fasteners such as A490 bolts or grooved pins are tested and certified to meet ASTM, ISO, or SAE standards, ensuring safe, reliable performance.
What is a Wedge Tensile Test?
Wedge tensile testing measures the tensile strength of metal fasteners, including custom rivets and metal thread inserts for wood, using a wedge under the fastener head. The test applies force until failure, verifying performance while ensuring the head-to-body junction remains intact. Passing confirms the fastener meets specification requirements for safe, reliable use in structural and industrial applications.
Why is Tensile Strength Testing Important?
Tensile strength testing shows how much force a metal fastener can handle before breaking. For swimming pool cover anchors, copper battery clamps, or structural bolts, verified tensile strength prevents failures, ensures safety, and avoids costly replacements or over-engineering.
What Are Bolt Grades and Standards?
Bolt grades determine mechanical properties such as tensile strength and hardness. Standards like ISO, ASTM, and SAE define the requirements for fasteners, including A325 bolts, A490 bolts, and heavy hex structural bolts. Selecting the right grade is essential for projects ranging from industrial metal fasteners to custom aerospace fasteners.
Bolt Grades Related to Strength
Bolt grades like A325n, A325sc, and A490 structural bolts define specific tensile strength, yield points, and proof loads. Choosing the right grade ensures metal fasteners handle stress safely, maintain structural integrity, and perform reliably in industrial and heavy-duty applications.
| Grade | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | Proof Load |
| Grade 1 | 60,000 psi (415 MPa) | 36,000 psi (250 MPa) | 33,000 psi (230 MPa) |
| Grade 2 | 74,000 psi (510 MPa) | 57,000 psi (395 MPa) | 55,000 psi (380 MPa) |
| Grade 5 | 120,000 psi (830 MPa) | 92,000 psi (635 MPa) | 85,000 psi (590 MPa) |
| Grade 8 | 150,000 psi (1,035 MPa) | 130,000 psi (895 MPa) | 120,000 psi (825 MPa) |
| Class 8.8 | 830 MPa (120,000 psi) | 640 MPa (93,000 psi) | 600 MPa (87,000 psi) |
| Class 10.9 | 1,040 MPa (151,000 psi) | 940 MPa (136,000 psi) | 830 MPa (120,000 psi) |
| Class 12.9 | 1,220 MPa (176,000 psi) | 1,220 MPa (176,000 psi) | 970 MPa (140,000 psi) |
Selecting the correct metal fastener grade prevents failures and ensures your engineering projects meet safety and performance standards.
How Do Tensile Strength, Proof Load, and Yield Strength Compare?
Understanding Tensile, Proof, and Yield Strength in Metal Fasteners
When selecting industrial metal fasteners, understanding tensile strength, proof load, and yield strength is crucial: tensile strength is the maximum force before breaking, proof load is the safe limit without deformation, and yield strength indicates when bending begins.
How These Strengths Relate to Fastener Performance
Tensile strength, proof load, and yield strength are all standardized measurements that determine a fastener’s grade or property class. They describe how much load a threaded fastener can bear when pulled from its head. Each term shows a different stress level: tensile strength is highest, yield strength is intermediate, and proof load is the safe minimum.
Why Understanding These Metrics Matters
Knowing these differences helps engineers choose the right metal fastener for safety-critical applications. Selecting a fastener with too low tensile strength risks breakage, while one rated too high may waste cost. Accurate understanding ensures reliable performance in construction, industrial machinery, and heavy-duty assemblies.
What Should Engineers Consider When Using Metal Fasteners?
When calculating bolt strength, engineers need to consider both material and environmental conditions. Metal fasteners like tab washers, threaded metal inserts for wood, or stainless steel threaded inserts can behave differently depending on temperature, humidity, and corrosion. Choosing the right fastener ensures durability and compliance.
Material Selection: The material directly affects tensile, shear, and proof loads. High-strength alloys handle heavier loads than standard carbon steels, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial metal fasteners used in bridges, structural frames, or machinery joints.
Bolt Grade: Selecting the correct grade, like A325 bolts, heavy hex bolts, or higher grades (10.9, 12.9), ensures the fastener can handle expected loads. Higher grades offer greater tensile and yield strength, critical for structural applications or high-stress conditions.
Thread Type: Threads impact load distribution. Fine threads handle higher tension, while coarse threads resist stripping in wood anchors or metal threaded inserts. Engineers must consider pitch and diameter to optimize strength and prevent fastener failure.
Preloading & Torque: Correct preloading ensures clamping without exceeding proof load, reducing fatigue and loosening. Proper torque-tightening is essential—under-tightening risks loosening, while over-tightening can cause bolt yielding. Charts and software tools help achieve precise results.
Environmental Factors: Corrosion, vibration, and temperature extremes can reduce fastener strength over time. Using stainless steel threaded inserts, copper battery clamps, or coated heavy hex bolts improves longevity, reliability, and safety for industrial and structural applications.
How Can Welleshaft Help With Metal Fasteners?
Welleshaft offers custom solutions for industrial fasteners. Whether you need custom standoffs, grooved pins, or high-strength A490 bolts, we provide manufacturing, testing, and certification. Our services guarantee reliable metal fastening systems for any application.
How to Get Quality Fasteners Manufactured to Your Specifications?
Simply provide your load requirements and preferred materials, and get fasteners designed, produced, and tested to spec. From bolts and rivets to threaded inserts and washers, every metal fastener is verified for tensile strength, shear strength, and proof load.
Whether you need per-spec bolts, custom rivets, or limited-run threaded inserts, we can handle it. Share your blueprints, and receive the exact quantity, size, and quality of industrial metal fasteners your project demands—no compromises.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fasteners
Where is the Strength of a Bolt Indicated?
Typically on the head or in accompanying certification documents. For example, A325 bolts have markings showing grade and manufacturer.
What Factors Affect Bolt Strength?
Material, thread type, diameter, environment, and load application all matter. Using Welleshaft-certified industrial metal fasteners reduces risk.
How is a High Strength Bolt Identified?
Look for standardized markings like A490, A325n, or stamped head numbers. High-strength bolts are used in critical structural applications and require certified proof load testing.
This blog was provided by the Welleshaft Engineering Team. Mr. Xu, with over 20 years of hands-on experience in industrial fasteners, leads the team in delivering high-quality solutions for structural bolts, rivets, threaded inserts, and washers. Welleshaft ensures every fastener meets tensile strength, shear strength, and proof load requirements, helping engineers and manufacturers maintain safety, compliance, and reliability across all applications.

