Materials Standards for PM Structural Parts Released
Powder metallurgy (PM) is a critical manufacturing method, revolutionizing how structural parts are made across various industries. Using PM techniques makes parts cheaper, better, and faster. Following strict material guidelines ensures high quality and reliability. The recent PM Structural Parts Released update—MPIF Standard 35—is a big deal. It provides detailed rules for making PM parts, helping manufacturers like Welleshaft achieve the best results with precision and consistency.
The MPIF (Metal Powder Industries Federation) standards cover a wide range of material types used in powder metallurgy for structural parts. Here are some common material types along with their applications and functions:
PM Copper-Based Materials
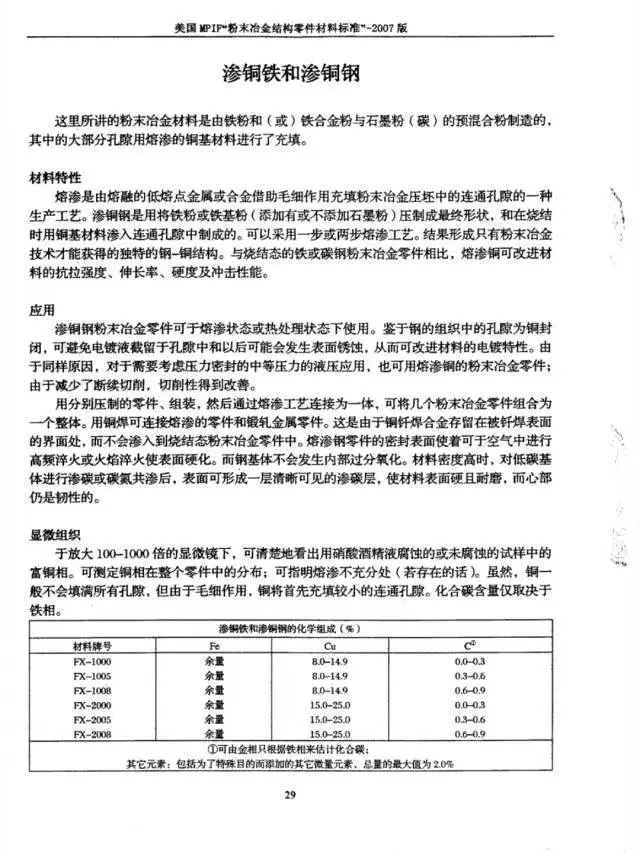
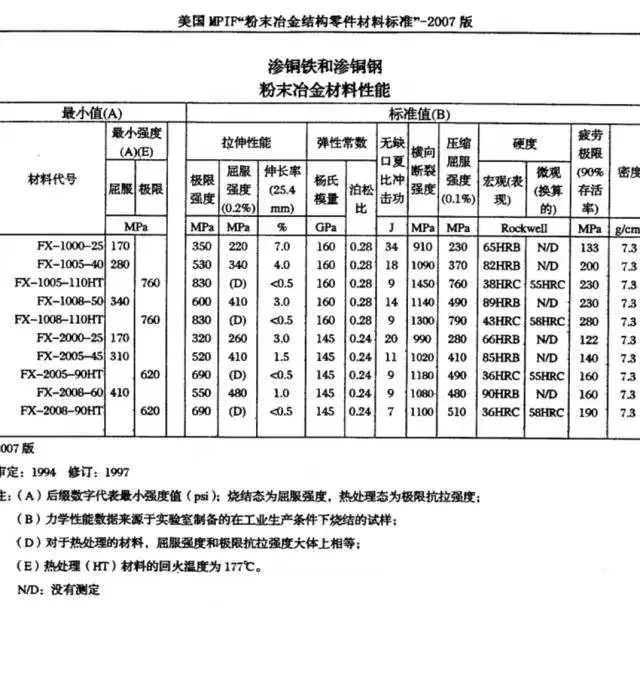
PM Iron-Based Materials
Function: These materials provide high strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability, making them suitable for components subjected to heavy loads and harsh operating conditions.
Application: Iron-based materials are widely used in automotive, industrial machinery, and consumer goods applications due to their excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness.
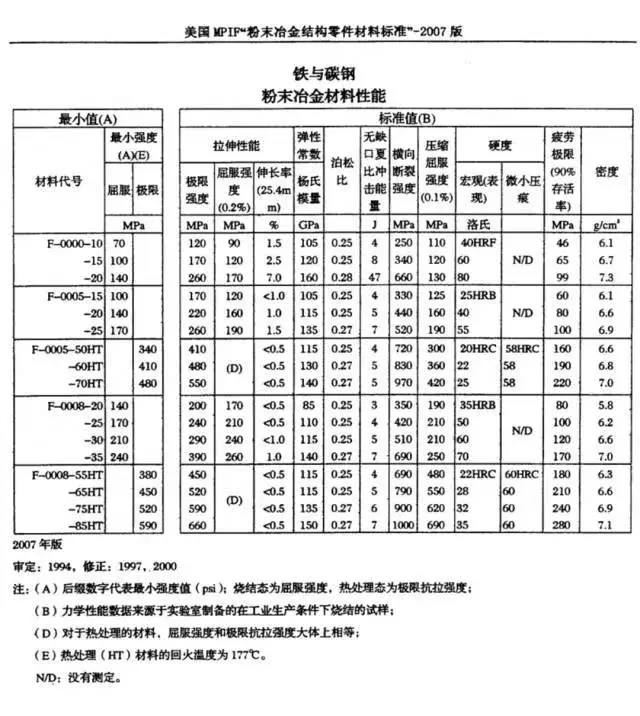
PM Nickel-Based Materials
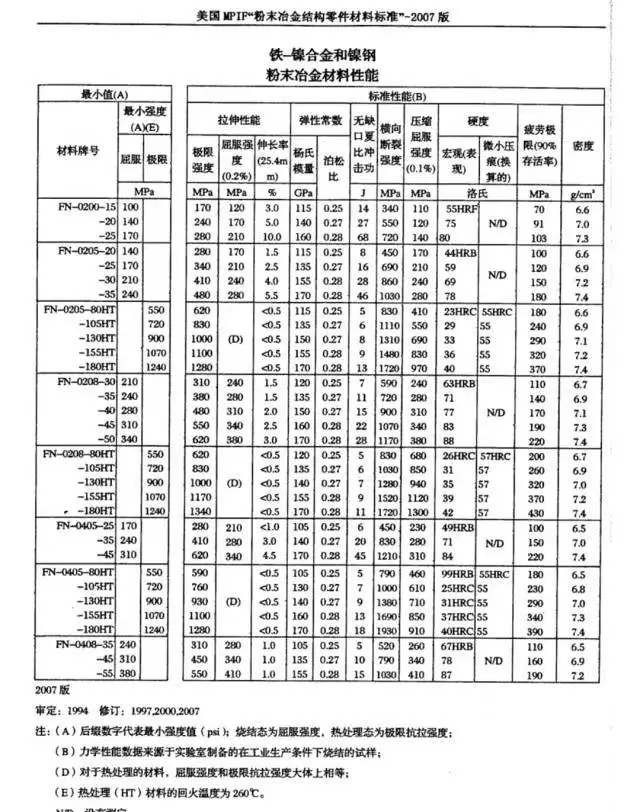
PM Steel-Based Materials
Function: Steel-based materials offer superior mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and toughness, making them ideal for structural components requiring durability and reliability.
Application: Steel-based materials find applications in automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment due to their versatility and strength-to-weight ratio.
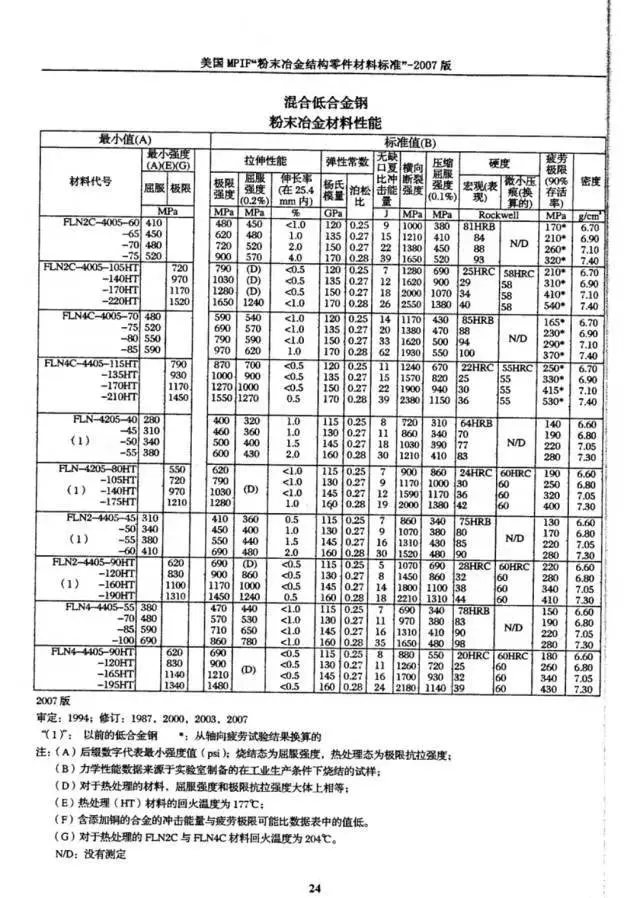
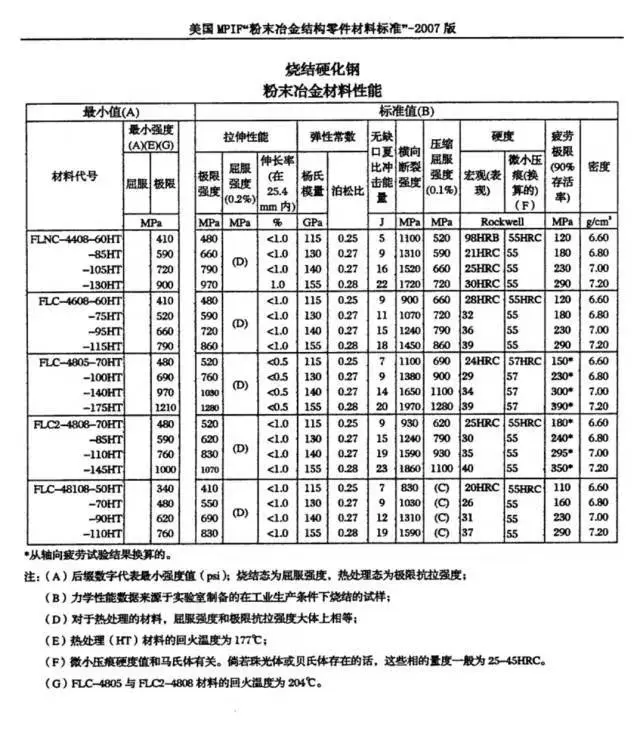
MPIF Material Sintering Types
Key Material Guidelines Ensure Quality in Powder Metallurgy (PM)
Welleshaft follows strict material guidelines to guarantee high quality, performance, and reliability in powder metallurgy structural parts.
Metal Sintering Forms Strong, Solid Components
Metal powders compact and heat to form strong parts with enhanced mechanical properties through metal sintering.
Selective Laser Sintering Powder Creates Complex Shapes
Selective laser sintering powder melts layers precisely, enabling complex geometry fabrication with high accuracy.
Powder Forming Shapes Materials Before Final Processing
Powder forming techniques, like compaction and extrusion, shape powders into forms before sintering or molding.
Mechanical or hydraulic presses compress powders into shapes, ensuring uniform density and material integrity.
Metal Injection Molding Combines Precision and Flexibility
Welleshaft uses metal injection molding to produce complex, high-precision components efficiently from powdered materials.
Powder Sintering Bonds Powders Below Melting Point
Heating compacted powders below melting point causes bonding, creating solid parts with improved strength.
Isostatic Compaction Applies Uniform Pressure All Around
Isostatic compaction exerts equal pressure from all directions to ensure consistent density and strong structure.
Cold Isostatic Compaction Shapes Powders at Room Temperature
Applying high pressure in liquid medium at room temperature helps form complex shapes with minimal defects.
Powder Metallurgy Offers Cost-Effective, Complex Manufacturing
PM techniques enable Welleshaft to fabricate cost-efficient metal parts with complex designs and excellent material use.
Welleshaft Maximizes Every PM Step for Quality Parts
From pre-sintering to post-processing, Welleshaft follows material guidelines to produce innovative, high-quality components.

