Precision Metal Molding Solutions | High-Quality Metal Molding Services
Metal molding is a vital manufacturing process, providing high-precision and complex metal parts for various industries. In this article, we’ll delve into the different types of metal molding processes, their advantages, applications, and how they compare to other metal forming methods. We’ll also explore key aspects such as equipment, materials, and common questions related to the process. Whether you’re in automotive, medical, or electronics manufacturing, understanding Precision Metal Molding Solutions can help you choose the right approach for your production needs.
Section 1 : Introduction
1.1.What is Molding in Metal?
Molding in metal refers to the process of shaping metal parts by using molds. These molds can be made from various materials such as sand, clay, or metal itself. The process involves pouring molten metal into the mold, allowing it to cool and solidify, and then removing the mold to reveal the final product. As part of Precision Metal Molding Solutions, this method enables manufacturers to produce accurate, high-quality components tailored to complex design requirements across diverse industries.
1.2.What is Molding Metal Called?
The term “molding metal” generally refers to the broader category of metal forming processes, including metal injection molding (MIM), die casting, sand casting, and more. Each method has its unique advantages and applications.
1.3.Metal Molding Materials
Metal molding involves shaping molten metal into desired forms using molds. It is a critical process in manufacturing industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, offering advantages such as precision, repeatability, and the ability to produce complex geometries.
1.3.1.Types of Metal Molding Materials
Ferrous Metals
Ferrous metals contain iron and are known for their strength and durability. They include:
- Steel: Highly versatile and commonly used due to its strength and flexibility.
- Stainless Steel:Commonly used in MIM for its strength and corrosion resistance.
- Cast Iron: Known for its excellent fluidity and castability, used in heavy-duty applications.
Non-Ferrous Metals
Non-ferrous metals do not contain iron and are typically more resistant to corrosion and lighter in weight. They include:
- Aluminum: Widely used in die casting for its lightweight and good mechanical properties.
- Copper Alloys:Excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Brass: Often used in sand casting for its excellent machinability and durability.
- Magnesium: The lightest structural metal, used where weight reduction is critical.
- Titanium: Used in investment castingand MIM for its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
1.3.2.Selection Criteria for Metal Molding Materials
When selecting materials for metal molding, consider the following factors:
Mechanical Properties: Strength, hardness, ductility, and toughness.
Thermal Properties: Melting point, thermal conductivity, and expansion.
Corrosion Resistance: Suitability for the intended environment and exposure.
Weight: Importance of material weight in the final application.
Cost: Material cost and economic feasibility for the project.

Section 2 : Types of Metal Molding
2.1.Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
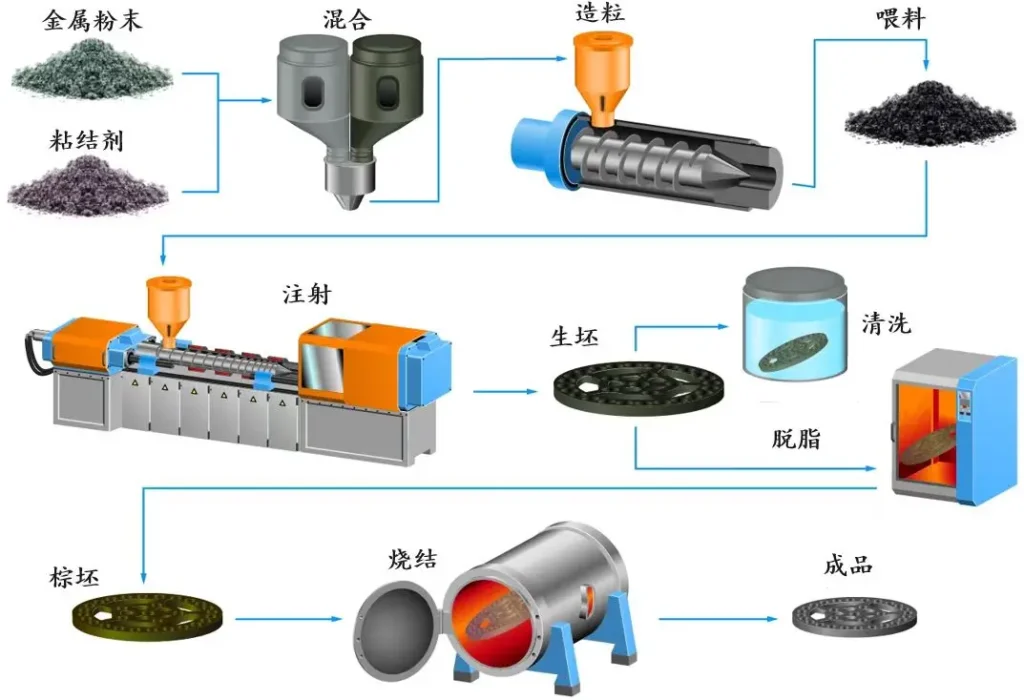
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a process that combines the flexibility of plastic injection molding with the strength and integrity of metal. Fine metal powders are mixed with a binder material to create a feedstock, which is then injected into a mold. The molded part is then subjected to a series of processes to remove the binder and sinter the metal.
Advantages of MIM:
- High precision and complex geometries
- Suitable for small to medium-sized parts
- High production efficiency
2.2.Die Casting
Die casting involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. This process is suitable for high-volume production and produces parts with excellent dimensional accuracy and smooth surfaces.
Advantages of Die Casting:
- High production rate
- Excellent surface finish
- Suitable for large and complex parts
2.3.Sand Casting
Sand casting uses sand as the mold material. It is one of the oldest metal forming techniques and is still widely used for producing large metal parts.
Advantages of Sand Casting:
- Low cost for small batches
- Versatility in material selection
- Suitable for large parts
2.4.Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, involves creating a wax model of the part, coating it with a ceramic shell, and then melting away the wax to leave a cavity for the molten metal.
Advantages of Investment Casting:
- High precision and surface finish
- Suitable for complex and detailed parts
- Versatility in material selection

Section 3 : Metal Injection Molding Process
The MIM process involves several key steps:
- Feedstock Preparation: Fine metal powders are mixed with a binder material to create a feedstock.
- Injection Molding: The feedstock is injected into a mold cavity, forming a “green” part.
- Debinding: The binder is removed from the molded part through chemical or thermal processes.
- Sintering: The debound part is heated in a furnace to bond the metal particles together, creating a dense and solid part.
Section 4 : What is the Difference Between Casting and MIM?
While both casting and MIM involve shaping metal parts, they differ in several ways:
- Material State:Casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold, whereas MIM uses metal powders mixed with a binder.
- Part Complexity: MIM can produce more intricate and precise parts compared to traditional casting methods.
- Production Volume:MIM is more suited for high-volume production of small to medium-sized parts, while casting can handle larger parts and varying production volumes.
4.1.MIM vs. Die Casting
- Precision: MIM offers higher precision and complex geometries compared to die casting.
- Material Range: MIM can work with a broader range of materials, including high-performance alloys.
- Surface Finish: Die casting generally provides a better surface finish, but MIM parts can be finished through additional processes.
Section 5 : Metal Molding Machines
The machinery used in metal molding varies depending on the specific process:
1.Metal Injection Molding Machine
MIM machines are similar to plastic injection molding machines but are designed to handle metal powders and binders. Key components include an injection unit, mold, and sintering furnace.
2.Die Casting Machine
Die casting machines consist of a furnace to melt the metal, a casting unit to inject the metal into the mold, and a clamping unit to hold the mold in place during the process.
3.Sand Casting Equipment
Sand casting requires molds made from sand, a furnace to melt the metal, and tools to pour the metal into the molds.

Section 6 : Applications of Metal Molding
1.Automotive Industry
Metal molding is widely used in the automotive industry to produce components such as engine parts, transmission gears, and structural components.
2.Medical Devices
MIM is particularly suitable for medical devices due to its ability to produce small, complex, and high-precision parts such as surgical instruments and orthopedic implants.
3.Consumer Electronics
Metal molding processes are used to manufacture components for smartphones, laptops, and other consumer electronics, providing durability and precision.
4.Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies on metal molding for producing lightweight, high-strength components that can withstand extreme conditions.
Section 7 : Cost Considerations
1.Metal Injection Molding Cost
The cost of MIM depends on factors such as material, complexity, and production volume. While the initial tooling cost is high, the per-part cost decreases significantly with higher volumes.
2.Metal Molding Machine Price
The price of metal molding machines varies based on the type and specifications. MIM machines can range from $100,000 to over $1 million, depending on their capabilities.

Section8 : Frequently Asked Questions
8.1.What is the MIM Process of Metal?
The MIM process involves mixing metal powders with a binder, injecting the mixture into a mold, removing the binder, and sintering the part to achieve full density.
8.2.What is the Metal Molding Method?
The metal molding method refers to various techniques used to shape metal parts using molds, including MIM, die casting, sand casting, and investment casting.
8.3.What is Molded Metal?
Molded metal refers to metal parts that have been shaped using a mold, resulting in precise and complex geometries.
8.4.What is Molding Metal Trim?
Molding metal trim involves creating decorative or protective metal strips used in various applications, such as automotive and architectural components.
8.5.What is the Difference Between MIM and Die Casting?
MIM uses metal powders mixed with a binder, while die casting involves injecting molten metal into a mold. MIM offers higher precision and complexity, while die casting is suitable for larger parts and higher production rates.
Conclusion
Metal molding processes, including MIM, die casting, sand casting, and investment casting, offer versatile solutions for producing high-precision and complex metal parts. Each method has its advantages and applications, making metal molding a critical technology in industries such as automotive, medical, consumer electronics, and aerospace.
For high-quality metal molding services, consider partnering with a trusted supplier like Welleshaft. Their expertise and commitment to quality ensure superior craftsmanship and exceptional performance in every project.