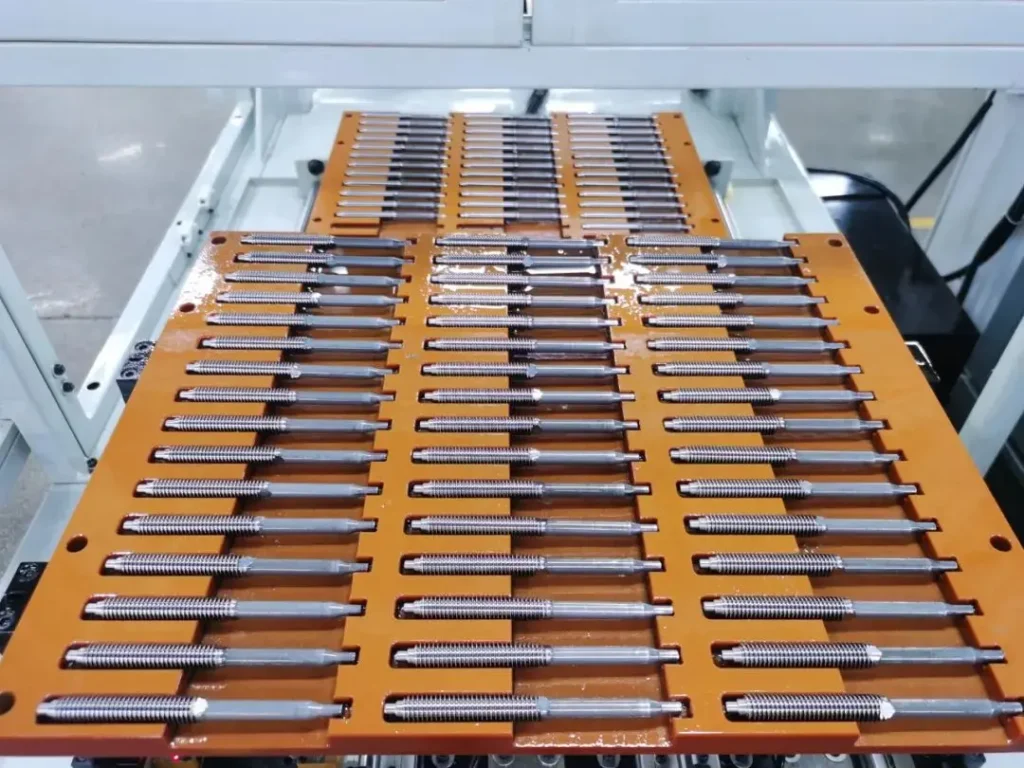
High-Quality ACME Threaded Products | Precision, Durability, and Performance
When it comes to mechanical components, High-Quality ACME Threaded Products stand out for their precision, durability, and performance. Whether you work in manufacturing or take on DIY projects, understanding ACME threads and their applications can significantly enhance your work’s efficiency and reliability. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of High-Quality ACME Threaded Products, including their types, applications, and advantages, while addressing common questions.
What Does ACME Stand for in Threads?
The ACME thread form, featuring a 29-degree thread angle, provides a strong, durable, and efficient threading system ideal for power transmission and heavy-load applications. These characteristics make High-Quality ACME Threaded Products essential components in demanding industrial settings.
What is an ACME Threaded Rod?
An ACMEthreaded rod is a long, straight metal rod with ACME threads running its length. These rods are essential in various mechanical applications, such as lead screws for machinery, linear actuators, and jacks. They offer superior load-bearing capacity and reduced backlash, making them a preferred choice in precision machinery.
Types of ACME Threaded Products
ACME threaded products come in various forms, each designed for specific applications. Common types include:
Standard ACME Threads: Widely used for general-purpose lead screws.
Stub ACME Threads: Have a shallower depth and are used where space constraints exist.
Centralizing ACME Threads: Designed to reduce backlash by ensuring more accurate alignment.

ACME Thread Chart and Dimensions
Understanding the dimensions of ACME threads is crucial for selecting the right product for your needs. Here is a detailed ACME thread chart:
- Pitch Diameter: The diameter of the thread at which the width of the thread and the space between threads are equal.
- Thread Height: 0.5 x Pitch (The height from the root to the crest of the thread.)
- Thread Angle: 29 degrees (The angle between the sides of the thread measured in an axial plane.)
- Lead: The distance a nut will travel parallel to the screw axis in one revolution.
- Root Diameter: The diameter at the base of the thread.
ACME Thread Sizes (INCH):
| ACME Thread Sizes (Inch) | Pitch Diameter (inch) | Major Diameter (inch) | Minor Diameter (inch) | Thread Height (inch) | Thread Angle |
| 1/4″ – 16 TPI | 0.2366″ | 0.2500’’ | 0.2233’’ | 0.0125″ | 29 degrees |
| 3/8″ – 12 TPI | 0.3481’’ | 0.3750’’ | 0.3218’’ | 0.0260’’ | 29 degrees |
| 1/2″ – 10 TPI | 0.4596″ | 0.5000’’ | 0.4203’’ | 0.0400″ | 29 degrees |
| 5/8″ – 8 TPI | 0.5721’’ | 0.6250’’ | 0.5178’’ | 0.0625’’ | 29 degrees |
| 3/4″ – 6 TPI | 0.6846″ | 0.7500’’ | 0.6153’’ | 0.0833″ | 29 degrees |
| 1″ – 5 TPI | 0.8987’’ | 1.0000″ | 0.8012’’ | 0.1250″ | 29 degrees |
| 1-1/4″ – 4 TPI | 1.1360″ | 1.2500″ | 1.0239’’ | 0.1875″ | 29 degrees |
| 1-1/2″ – 3 TPI | 1.3865″ | 1.5000″ | 1.2396’’ | 0.3333″ | 29 degrees |
| 2″ – 2 TPI | 1.9375″ | 2.0000’’ | 1.8015’’ | 0.5000″ | 29 degrees |
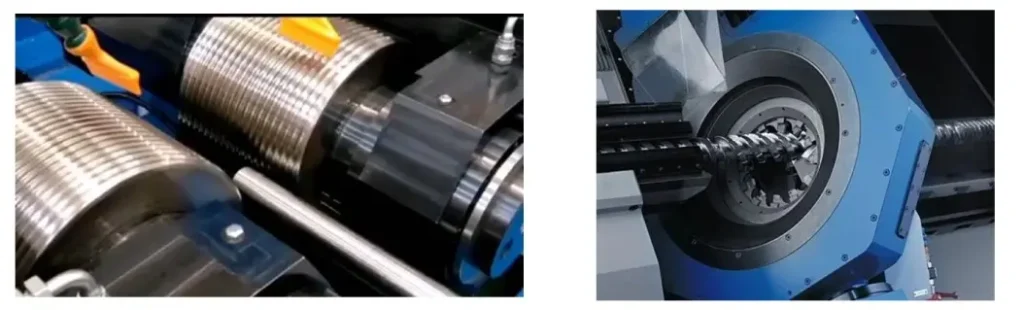
ACME Thread Sizes (Metric):
For metric sizes, the dimensions vary similarly, ensuring compatibility with international standards as below:
| ACME Thread Sizes (Metric) | Pitch Diameter (mm) | Major Diameter (mm) | Minor Diameter (mm) | Thread Height (mm) | Thread Angle |
| 6 mm – 3 mm Pitch | 5.0 | 6.0 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 29 degrees |
| 10 mm – 2 mm Pitch | 9.0 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 1.0 | 29 degrees |
| 12 mm – 4 mm Pitch | 10.0 | 12.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 29 degrees |
| 16 mm – 5 mm Pitch | 14.0 | 16.0 | 12.0 | 2.5 | 29 degrees |
| 20 mm – 4 mm Pitch | 18.0 | 20.0 | 16.0 | 2.0 | 29 degrees |
| 25 mm – 5 mm Pitch | 23.0 | 25.0 | 21.0 | 2.5 | 29 degrees |
| 30 mm – 6 mm Pitch | 27.0 | 30.0 | 24.0 | 3.0 | 29 degrees |
| 35 mm – 6 mm Pitch | 32.0 | 35.0 | 29.0 | 3.0 | 29 degrees |
| 40 mm – 7 mm Pitch | 36.5 | 40.0 | 33.0 | 3.5 | 29 degrees |
| 45 mm – 8 mm Pitch | 41.0 | 45.0 | 37.0 | 4.0 | 29 degrees |
| 50 mm – 8 mm Pitch | 46.0 | 50.0 | 42.0 | 4.0 | 29 degrees |
| 55 mm – 9 mm Pitch | 50.5 | 55.0 | 46.0 | 4.5 | 29 degrees |
| 60 mm – 9 mm Pitch | 55.5 | 60.0 | 51.0 | 4.5 | 29 degrees |

ACME Thread Types and Materials
Steel (Carbon, Alloy, Stainless) ACME Rod: Offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability, used in heavy-duty applications.
Brass ACME Threaded Rod: Known for its corrosion resistance and non-sparking properties, used in environments where non-rusting materials are required.
Aluminum ACME Threaded Rod: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, used where weight is a critical factor.
Plastic (Acetal, Nylon) ACME Threaded Rod: Low friction, Used in lightweight and non-conductive applications.
Applications of ACME Threaded Products
ACME threaded products are utilized in a wide range of applications, including:
- Lead Screws: Used in machines to translate turning motion into linear motion.
- CNC Machines:Precision machinery that uses lead screws for accurate movement control.
- Jacks and Lifts: Used to lift heavy loads with mechanical advantage.
- Linear Actuators:Devices that convert rotational motion into linear motion.
- Presses: Used in manufacturing to shape or cut materials.
- Valve Stems: Used in valves to open or close the flow of fluid.
- Garage Door Openers: Used to translate the rotational motion of the motor into the linear motion needed to open or close the door.
Advantages of ACME Threaded Products
High Load-Bearing Capacity: Suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Reduced Backlash: Ensures precision in motion control.
Durability: Resistant to wear and tear, providing a long service life.
Why Choose Welleshaft for ACME Threaded Products
Albero a pozzo delivers precision-engineered ACME threaded rods and nuts, combining high load-bearing capacity, smooth linear motion, and durable materials. With strict quality control, diverse sizes, and custom solutions, Welleshaft ensures reliable performance for industrial machinery, automation systems, and motion-critical applications worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What Are the Advantages of ACME Threads?
They offer higher load capacity, less backlash, and greater durability than standard threads, ideal for demanding uses. -
How Do ACME Threads Differ from Trapezoidal Threads?
Trapezoidal threads, common in Europe, have a 30-degree angle; ACME threads have a 29-degree angle and are more common in the U.S. -
What Is the Relationship Between ACME Threads and Lead Screws?
ACME threads are one type of lead screw thread. Lead screws can have various profiles like ACME, trapezoidal, or square. -
What Is the Origin of ACME Threads?
The ACME Manufacturing Company standardized these threads to create a stronger, more efficient system.
This blog was provided by the Albero a pozzo Engineering Team, Mr. Xu. With years of expertise in mechanical components and precision motion systems, Welleshaft ensures high-quality ACME threaded products, helping engineers and manufacturers achieve reliable and efficient industrial solutions.