Nickel alloy fasteners, including Inconel and Monel bolts, are critical components in industries like oil & gas, marine, automotive, and chemical plants. Even though these alloys resist corrosion, exposure to saltwater, chemicals, or high temperatures can degrade their surfaces, leading to maintenance issues, shipment delays, and increased operational costs. Selecting the right advanced coatings and surface finishes for nickel alloy fasteners is essential for ensuring corrosion protection, wear resistance, and long-term reliability.
International clients frequently ask: Which coating type—PVD, electroless nickel, or passivation—is most suitable for their applications? What is the recommended coating thickness and surface preparation? How can third-party inspection in China ensure consistent quality?
As a solutions expert in high-performance and specialty material fasteners, WELLESHAFT provides not just products but comprehensive guidance: from material selection to coating technology, ISO-certified third-party inspection, and compliance with ASTM B117, ISO 9227, and GB/T 1696 standards. By leveraging WELLESHAFT’s expertise, companies can extend fastener lifespan, reduce operational costs, and enhance global brand reputation.
Why Nickel Alloy Fasteners Fail in Harsh Environments
Environmental Stressors Impacting Nickel Alloy Fasteners
-
Marine fasteners: salt spray → pitting, micro-cracks
-
Oil & gas fasteners: chemical exposure, temperature-induced oxidation
-
Automotive/EV brake and suspension fasteners: friction loss, wear without proper coating
Operational and Cost Implications
-
Premature degradation increases maintenance costs
-
Shipment delays occur when coatings fail inspection or delaminate
-
Repeated failures may erode trust and prompt supplier switching
Real International Client Scenario
A USA marine OEM adopted PVD-coated Inconel bolts supplied and inspected by WELLESHAFT. Maintenance intervals extended from 6 months to 30 months, reducing service costs by 40%, demonstrating the value of combining advanced coatings with expert solution guidance and inspection.
Why Nickel Alloy Fastener Coatings Fail
Technical Causes
-
Improper coating selection: PVD, electroless nickel, and passivation have different strengths; choosing incorrectly accelerates wear
-
Poor surface preparation: Residual oils, micro-cracks, or inconsistent roughness reduce adhesion
-
Coating thickness inconsistency: ASTM B633 and ISO 9227 define thickness ranges (Electroless Ni 10–25 µm, PVD 2–5 µm)
-
Detection frequency: Batch testing per ASTM B117 and ISO 4628 ensures consistent quality
Management & Process Causes
-
Lack of standardized inspection protocols
-
Weak supplier QA systems not following ISO 3506
-
Inefficient documentation and batch tracking
Industry Impact: Cost, Delivery, Quality, and Brand
| Impact Area | Description | Real-World Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Rework, replacement, downtime | Offshore platform fasteners replaced every 6 months instead of 3–5 years |
| Delivery | Shipment delays | Automotive OEM brake bolts delayed 2 weeks due to failed coating inspection |
| Quality | Friction coefficient reduction, warranty claims | Coefficient dropped below 0.32, requiring bolt replacement |
| Brand | Reduced international trust | Clients switch to suppliers with tested corrosion-resistant fasteners |
Cost-saving Example
A European chemical plant reduced fastener replacement costs by $120,000/year after switching to Welleshaft electroless nickel coatings with third-party inspection.
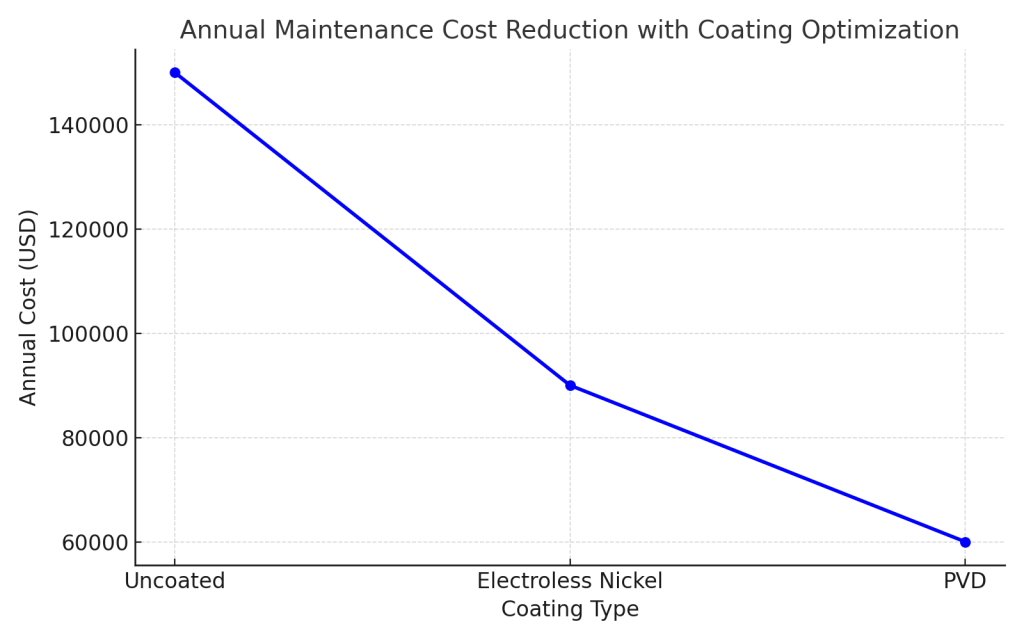
PVD vs Electroless Nickel: Coatings for Nickel Alloy Fasteners
| Coating Type | Average Service Life | Corrosion Resistance | Wear Resistance | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncoated Nickel Alloy | 6–12 months | Low | Medium | Temporary or indoor use |
| Electroless Nickel (WELLESHAFT) | 36–60 months | High | High | Marine, automotive, industrial chemical exposure |
| PVD (WELLESHAFT) | 48–72 months | Very High | Very High | Offshore, high-temp, high-wear applications |
Friction Coefficient Comparison – Automotive Brake Bolts
| Coating | Initial µ | After 12 Months | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uncoated | 0.38 | 0.32 | Significant wear |
| Electroless Nickel (WELLESHAFT) | 0.39 | 0.37 | Minor degradation |
| PVD (WELLESHAFT) | 0.40 | 0.39 | Excellent retention |
Nickel Alloy Fasteners: Advanced Coatings & Surface Finishes Guide
Short-Term Measures by Welleshaft
-
Advanced Coating Selection: Welleshaft evaluates client-specific environments and recommends the optimal coating (PVD, electroless nickel, passivation) for corrosion and wear resistance.
-
Third-Party Inspection Services: ISO-certified lab in China, including adhesion testing, coating thickness measurement, ASTM B117 salt spray tests.
-
Immediate Issue Resolution: Identify defective coatings early and provide corrective measures, preventing shipment delays.
Long-Term Optimization Strategies by Welleshaft
-
Surface Preparation Expertise: Precision grit blasting, ultrasonic cleaning, controlled micro-roughness for maximum coating adhesion.
-
Custom Coating Thickness Control:
-
PVD (2–5 µm) – high wear, chemical and temperature resistance
-
Electroless Nickel (10–25 µm) – uniform corrosion protection
-
Passivation – nitric/citric acid treatment to remove free iron
-
-
Batch Testing & Quality Tracking: ASTM B117, ISO 4628, ISO 3506 inspections; results tracked for long-term consistency.
-
Supplier Audits & Process Improvement: Regular ISO 9001/ISO 3506 audits, KPI monitoring, QA staff training for continuous improvement.
Client Benefits:
-
Reduced maintenance costs, extended fastener lifespan
-
Enhanced reliability in harsh environments
-
Compliance assurance with international standards
-
Clear documentation and traceability for global supply chains
6. Case Studies: Real International Client Scenarios
Marine Fasteners – USA Offshore OEM
-
Problem: Corrosion, friction loss, inconsistent electroless nickel thickness
-
WELLESHAFT Solution: Full surface analysis → PVD coating → grit blasting/ultrasonic cleaning → ISO lab batch inspection → supplier QA support
-
Outcome: Maintenance interval extended 6 → 30 months, flaking <2%, costs ↓ 40%
Automotive Brake Bolts – European OEM
-
Problem: Premature wear, friction coefficient <0.32, warranty claims
-
WELLESHAFT Solution: Electroless nickel 10–25 µm, surface prep, batch inspection, documentation for FMVSS 135 compliance
-
Outcome: Friction coefficient restored to 0.39, return rates ↓ 25%, compliance achieved, enhanced brand reputation
FAQ – Advanced Coatings for Nickel Alloy Fasteners
-
Which coatings are best for marine applications?
PVD or electroless nickel; WELLESHAFT selects type & thickness (PVD 2–5 µm, Electroless Ni 10–25 µm). -
How does Welleshaft ensure consistent quality?
ISO-certified lab inspection, adhesion, thickness, ASTM B117, plus supplier audits and QA tracking. -
Can coatings extend maintenance intervals?
Yes. PVD or electroless nickel coatings inspected by WELLESHAFT can extend intervals from 6 months to 30 months. -
What standards apply?
ASTM B117, ISO 9227, ISO 3506, GB/T 1696. WELLESHAFT ensures full compliance. -
How often should coatings be inspected?
Every production batch; critical applications may require periodic re-testing. -
Can Welleshaft help reduce costs and improve ROI?
Yes. Optimized coatings, consistent quality, and defect prevention reduce maintenance, rework, and extend fastener life.
Call-to-Action (CTA)
Request a Quote for Nickel Alloy Fastener Coating Today with Welleshaft
Maximize corrosion and wear protection for nickel alloy fasteners through Welleshaft-certified coatings, expert inspection, and optimized surface finishing workflows.
For Further Reading
1.How to Achieve ±0.01 mm in Nickel Alloy Fasteners for USA/EU?
2.Nickel Alloy Fasteners: Materials, Manufacturing & Sourcing

