Pump Shafts: Find Durable & Reliable Shafts for Your Pumps
Pumps are the workhorses of countless industries, from water treatment and agriculture to manufacturing and oil & gas. At the heart of a pump’s operation lies the pump shaft, a critical component responsible for transferring rotational energy from the motor to the impeller or rotor, enabling the fluid to be moved. Choosing the right pump shaft is paramount for ensuring pump performance, longevity, and minimizing downtime. This article will explore the different types of pump shafts, the materials used in their construction, common failure modes, and guide you on how to select a durable and reliable shaft for your specific application.
Why Pump Shafts Matter
The pump shaft is more than just a rotating rod; it’s a precision-engineered component subjected to significant stress, vibration, and potentially corrosive environments. A weak or improperly selected shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in costly repairs, production delays, and even safety hazards. Consider these key factors when assessing the importance of the pump shaft:
Torque Transmission: The shaft must efficiently transmit the torque generated by the motor to the impeller or rotor, which in turn moves the fluid.
Bearing Support: The shaft provides a mounting surface for bearings, which support the rotating components and minimize friction.
Impeller/Rotor Support: The shaft securely holds the impeller or rotor in place, ensuring proper alignment and preventing imbalances.
Resistance to Bending and Deflection: The shaft must resist bending and deflection under load to maintain optimal pump performance and prevent seal damage.
Corrosion Resistance: Depending on the fluid being pumped, the shaft may need to withstand corrosive environments to prevent degradation and failure.
Types of Pump Shafts: A Comprehensive Overview
While the fundamental function remains the same, pump shafts are known by various names depending on the specific pump design and industry terminology. Here’s an overview of common pump shaft designations:
|
Shaft Type |
Description |
|
Axle (of the pump) |
A static shaft around which a wheel or component rotates. (Typically for very low-speed or static applications). |
|
Shaft (of a pump) |
The general term for a rotating member transmitting power. |
|
Arbor (of the pump) |
A shaft on which a cutting tool or workpiece is mounted. (Less common in standard pumps). |
|
Main Shaft (of a pump) |
The primary shaft that transmits power from the motor to the pump mechanism. |
|
Drive Shaft (of a pump) |
A shaft that transmits power from the motor or prime mover to the pump shaft. |
|
Rotor Shaft (of a pump) |
Specifically used in pumps with a rotating rotor, such as progressive cavity pumps. |
|
Impeller Shaft |
Used in centrifugal pumps, connecting the motor to the impeller. |
|
Drive Spindle |
Similar to a drive shaft, often used in smaller or specialized pumps. |
|
Transmission Shaft |
A shaft used within a gearbox or transmission system connected to the pump. |
|
Power Transfer Shaft |
General term for a shaft that transmits power. |
|
Rotating Element Shaft |
A shaft directly connected to a rotating component within the pump. |
|
Rotating Bar (of the pump) |
Similar to a shaft, this is the rotating member of the pump. |
|
Impeller Shaft |
Used in centrifugal pumps, connecting the motor to the impeller. |
|
Rotor Shaft (of a pump) |
Specifically used in pumps with a rotating rotor, such as progressive cavity pumps. |
|
Drive Spindle |
Similar to a drive shaft, often used in smaller or specialized pumps. |
|
Transmission Shaft |
A shaft used within a gearbox or transmission system connected to the pump. |
|
Power Transfer Shaft |
General term for a shaft that transmits power. |
|
Rotating Element Shaft |
A shaft directly connected to a rotating component within the pump. |
|
Rotating Bar (of the pump) |
Similar to a shaft, this is the rotating member of the pump. |
|
Spindle Shaft |
Used in a variety of pumping applications. |
Materials for Pump Shafts: Balancing Strength and Corrosion Resistance
The material used to manufacture a pump shaft is a critical factor determining its durability and resistance to various operating conditions. Common materials include:
Carbon Steel: Offers high strength and is suitable for general-purpose applications where corrosion is not a major concern. Often requires coatings for corrosion resistance.
Alloy Steel: Provides increased strength, toughness, and wear resistance compared to carbon steel. Alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum enhance specific properties.
Stainless Steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications involving water, chemicals, and other corrosive fluids. Different grades of stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316, 416) offer varying levels of corrosion resistance and strength.
Duplex Stainless Steel: Provides superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to standard stainless steel grades. Well-suited for harsh environments.
Other Materials: In specialized applications, shafts may be made from materials like titanium, bronze, or ceramic materials to meet specific performance requirements.
Common Causes of Pump Shaft Failure
Understanding the common failure modes of pump shafts is crucial for preventative maintenance and selecting the appropriate shaft for your application. Some frequent causes of failure include:
Fatigue: Repeated stress cycles can lead to fatigue cracks, eventually causing shaft failure. This is often exacerbated by misalignment, vibration, or improper balancing.
Corrosion: Exposure to corrosive fluids can weaken the shaft material, leading to pitting, cracking, and ultimately failure.
Erosion: The impact of abrasive particles in the fluid can erode the shaft surface, reducing its strength and increasing the risk of failure.
Overloading: Exceeding the shaft’s design load can cause bending, yielding, or fracture.
Misalignment: Improper alignment between the motor and the pump can induce excessive stress on the shaft, leading to premature failure.
Cavitation: Cavitation can lead to erosion which can damage pump shafts.
Improper Installation: Incorrect tightening of fasteners or improper fitting of components can create stress concentrations that lead to failure.
Selecting the Right Pump Shaft: Key Considerations
Choosing the correct pump shaft involves careful consideration of several factors:
Pump Type: The type of pump (e.g., centrifugal, positive displacement, submersible) will influence the shaft design and material requirements.
Fluid Properties: The fluid being pumped (e.g., water, chemicals, slurry) will dictate the necessary corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Operating Conditions: Factors such as temperature, pressure, speed, and vibration levels will affect the shaft’s performance and longevity.
Torque Requirements: The shaft must be able to transmit the required torque without exceeding its design limits.
Shaft Size and Dimensions: The shaft’s diameter, length, and keyway dimensions must be compatible with the pump’s design.
Material Selection: Choose a material that offers the appropriate strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance for the application.
Manufacturing Quality: Ensure the shaft is manufactured to high standards with precise tolerances and surface finishes.
Cost: Balance the cost of the shaft with its performance and durability requirements.

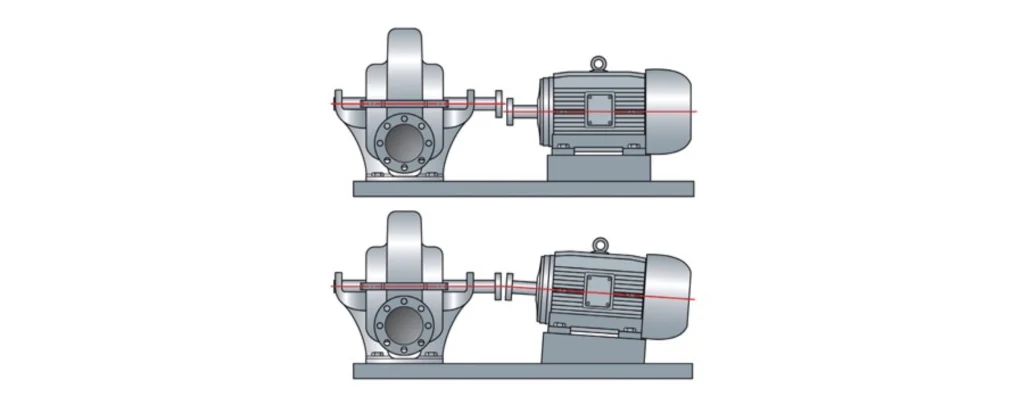
The Importance of Proper Pump Shaft Alignment
Proper pump shaft alignment is critical for minimizing stress on the shaft, reducing vibration, and extending the lifespan of bearings and seals. Misalignment can lead to:
Increased vibration and noise
Premature bearing and seal failure
Increased energy consumption
Shaft fatigue and failure
Regularly check and correct shaft alignment using precision alignment tools to prevent these problems.
Welleshaft: Your Trusted Partner for Durable and Reliable Pump Shafts
When it comes to sourcing high-quality pump shafts, Welleshaft stands out as a trusted global supplier and contract manufacturer. With years of experience in the industry, Welleshaft offers a comprehensive range of pump shafts designed to meet the demanding requirements of various applications.
Why Choose Welleshaft?
Wide Range of Materials: Welleshaft provides shafts made from various materials, including carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and duplex stainless steel, allowing you to select the perfect material for your specific needs.
Custom Manufacturing Capabilities: Welleshaft offers custom manufacturing services to create shafts tailored to your exact specifications. This includes custom dimensions, materials, and surface finishes.
Stringent Quality Control: Welleshaft adheres to strict quality control procedures throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring that every shaft meets the highest standards.
Competitive Pricing: Welleshaft offers competitive pricing without compromising on quality, making them an excellent value for your investment.
Global Reach: With a global presence, Welleshaft can efficiently supply pump shafts to customers worldwide.
Expert Technical Support: Welleshaft’s team of experienced engineers provides expert technical support to help you select the right shaft for your application and troubleshoot any issues.
Conclusion
The pump shaft is a critical component that plays a vital role in the performance and reliability of your pumps. By understanding the different types of shafts, materials, failure modes, and selection criteria, you can choose the right shaft for your specific application and ensure long-lasting pump performance. Partnering with a reputable supplier like Welleshaft will give you the confidence that you are receiving a durable, reliable, and high-quality pump shaft that meets your needs. Investing in a quality pump shaft is an investment in the efficiency, longevity, and overall success of your pumping system.

